Antineoplastic multi-drug chemotherapy to sensitize tumors triggers multi-drug resistance and inhibits efficiency of maintenance treatment in glioblastoma cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2022-5556Keywords:
Glioblastoma, multi-drug resistance, apoptosis, autophagy, angiogenesis, U87-MGAbstract
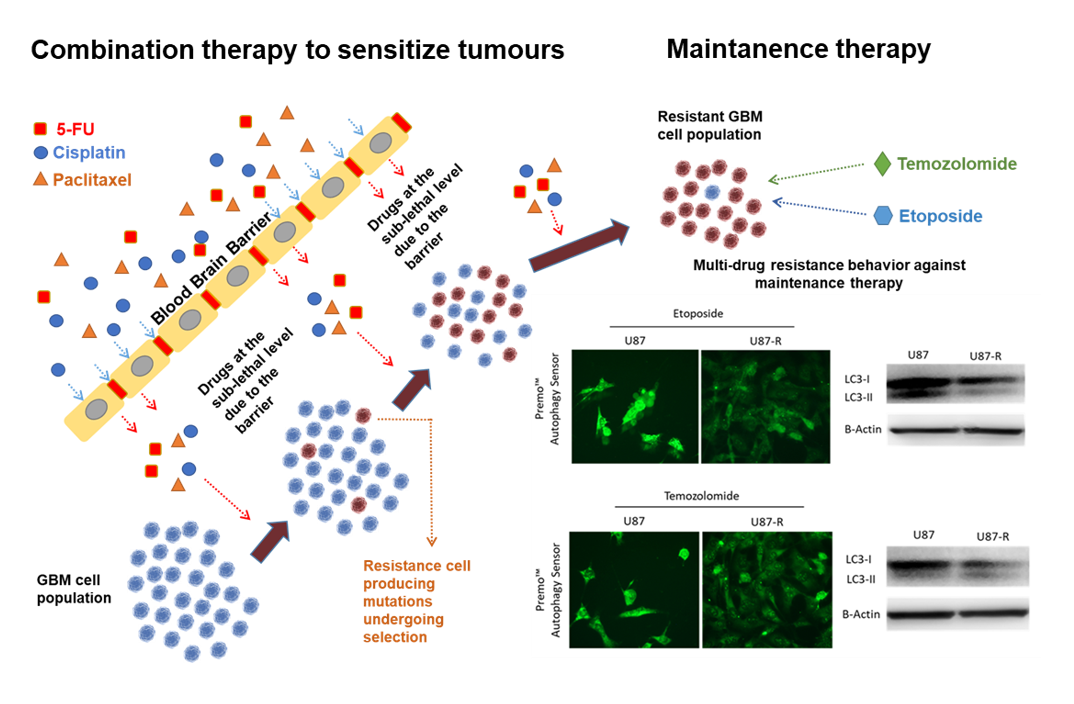
Combinations of the well-known antineoplastic agents 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu), cisplatin, and paclitaxel are employed to increase radiotherapy/immunotherapy efficacy against persistent and resistant tumors. However, data remains needed on the hormetic, chronic, and long-term side effects of these aggressive combination chemotherapies. Here we investigated cellular and molecular responses associated with these combined agents, and their potential to induce multi-drug resistance against the temozolomide (TMZ) and etoposide (EP) used in glioblastoma maintenance treatment. We analyzed resistance and survival signals in U87 MG cells using molecular probes, fluorescent staining, qRT-PCR, and immunoblot. Repeated treatment with combined 5-Fu, cisplatin, and paclitaxel induced cross-resistance against TMZ and EP. Resistant cells exhibited elevated gene/protein expression of MRP1/ABCC1, ABCC2, BRCP/ABCG2, and GST. Moreover, they managed oxidative stress, cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagy signaling to ensure survival. In these groups TMZ and etoposide efficiency dramatically reduced. Our result suggests that combined high-dose treatments of classical antineoplastic agents to sensitize tumors may trigger multi-drug resistance and inhibit maintenance treatment. When deciding on antineoplastic combination therapy for persistent/resistant glioblastoma, we recommend analyzing the long-term hormetic and chronic effects on cross-resistance and multi-drug resistance in primary cell cultures from patients.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Oguzhan Doganlar, Zeynep Banu Doğanlar, Suat Erdogan, Emre Delen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





