Effects of acute and chronic disease on cell junctions in mouse liver
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2022-5559Keywords:
adherens junctions, tight junctions, gap junctions, liver, acute liver disease, chronic liver diseaseAbstract
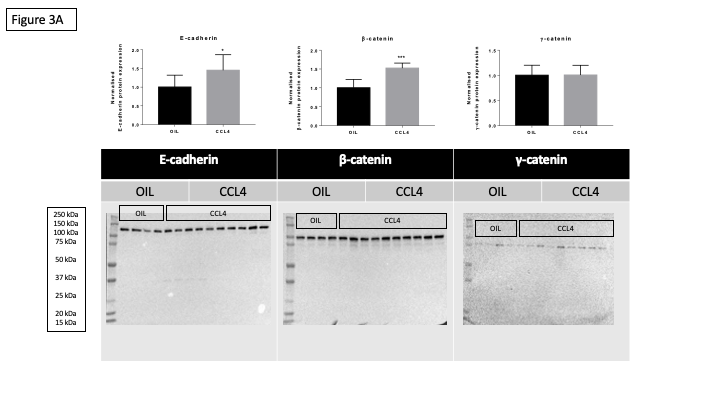
Cell junctions, including anchoring, occluding and communicating junctions, play an indispensable role in tissue architecture and homeostasis. Consequently, malfunctioning of cell junctions is linked with a wide range of disorders, including in liver. The present study was set up to investigate the effects of acute and chronic disease induced by chemical compounds on hepatic cell junctions in mice. Mice were either overdosed with paracetamol or repeatedly administered carbon tetrachloride followed by sampling at 24 hours or 8 weeks, respectively. mRNA and protein expression levels of adherens, gap and tight junction components were measured in liver using reverse transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis and immunoblot techniques, respectively. It was found that protein levels of the adherens junction building blocks β-catenin and γ-catenin, the gap junction components Cx26 and Cx32, and the tight junction constituent zonula occludens 2 were decreased, while mRNA levels of the adherens junction building block E-cadherin, and the tight junction constituent zonula occludens 2 and claudin 1 were upregulated following paracetamol overdosing. Repeated administration of carbon tetrachloride increased protein levels of E-cadherin, β-catenin, Cx26, Cx32, Cx43 and claudin 1. The latter was reflected at the mRNA level. In conclusion, acute and chronic liver disease have different effects on cell junctions in liver.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Raf Van Campenhout, Bruno Cogliati, Mathieu Vinken

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





