Mixture effects of co-formulants and two plant protection products in a liver cell line
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2022-5648Keywords:
mixture effects, plant protection product, liver toxicity, co-formulants, Cytochrome P450 enzymesAbstract
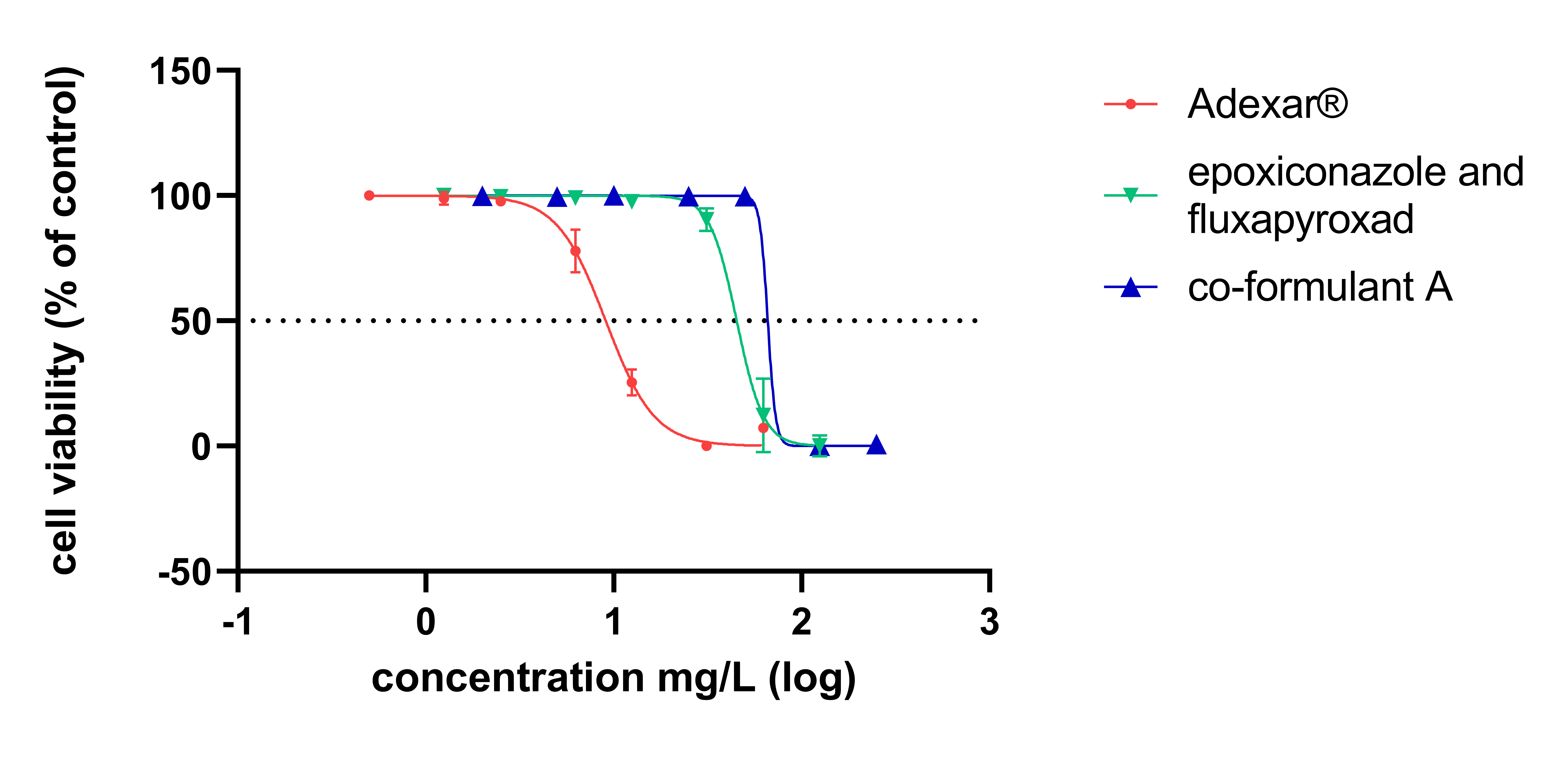
Plant protection products (PPPs) consist of one or more active substances and several co-formulants. Active substances provide the functionality of the PPP and are consequently evaluated according to standard test methods set by legal data requirements before approval, whereas co-formulants’ toxicity is not as comprehensively assessed. However, in some cases mixture effects of active substances and co-formulants might result in increased or different forms of toxicity. In a proof-of-concept study we hence built on previously published results of Zahn et al. (2018) on the mixture toxicity of Priori Xtra® and Adexar® to specifically investigate the influence of co-formulants on the toxicity of these commonly used fungicides. Products, their respective active substances in combination as well as some co-formulants were applied to human hepatoma cell line (HepaRG) in several dilutions. Cell viability analysis, mRNA expression, abundance of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes and intracellular concentrations of active substances determined by LC-MS/MS analyses demonstrated that the toxicity of the PPPs is influenced by the presence of co-formulants in vitro. PPPs were more cytotoxic than the mix of their active substances. Gene expression profiles of cells treated with the PPPs were similar to those treated with their respective mixture combinations with marked differences. Co-formulants can cause gene expression changes on their own. LC-MS/MS analyses revealed higher intracellular concentrations of active substances in cells treated with PPPs compared to those treated with the respective active substances’ mix. Proteomic data showed co-formulants can induce ABC transporters and CYP enzymes. Co-formulants can contribute to the observed increased toxicity of PPPs compared to their active substances in combination due to kinetic interactions, necessitating a more comprehensive evaluation approach.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Katreece Feiertag, Mawien Karaca, Benjamin Fischer, Tanja Heise, Denise Bloch, Tobias Opialla, Tewes Tralau, Carsten Kneuer, Philip Marx-Stoelting

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





