Remifentanil does not affect human microglial immune activation in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2022-5667Keywords:
human microglia, remifentanil, hyperalgesia, Interleukin-6, Interleukin-8, monocyte chemotactic protein 1Abstract
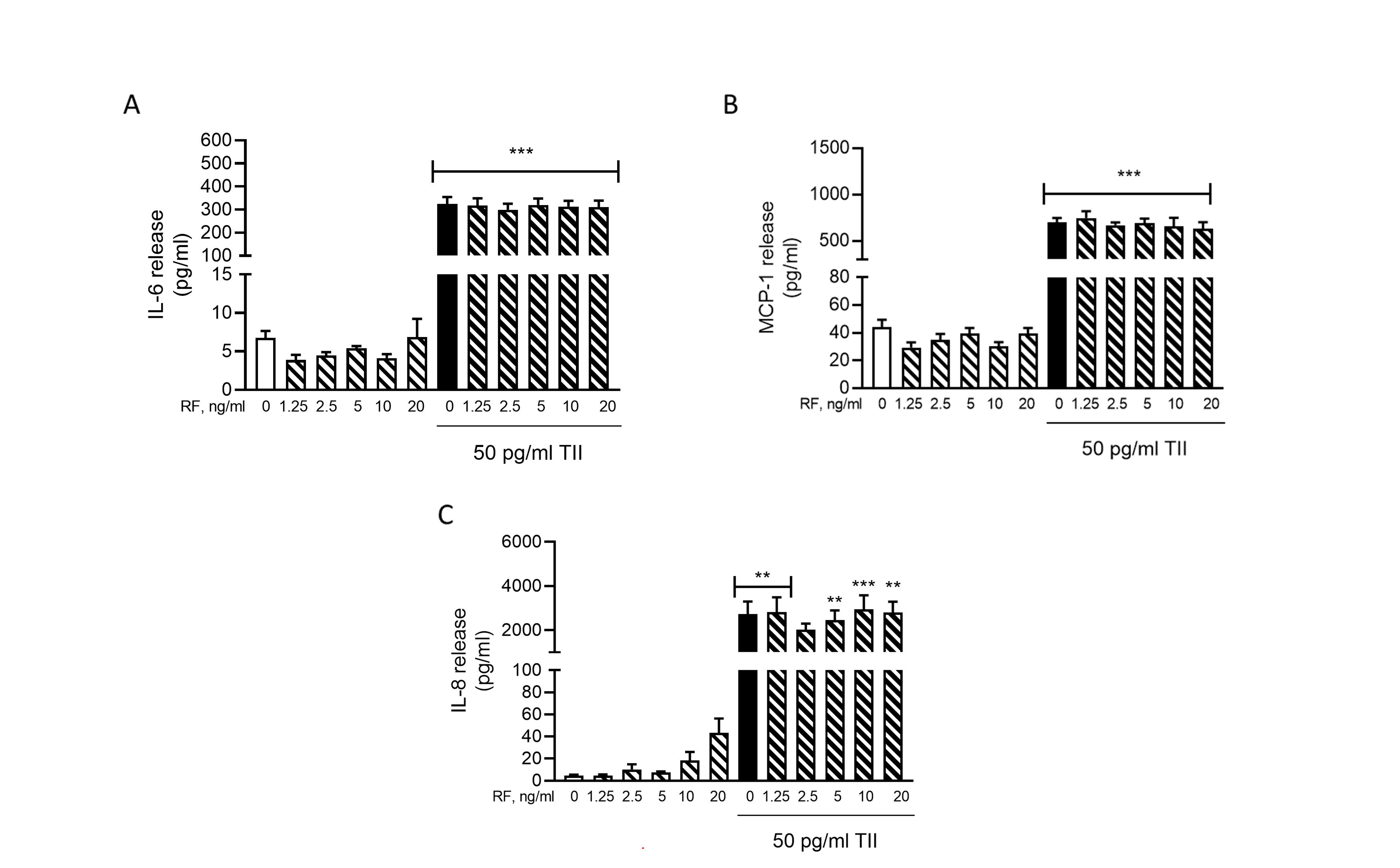
Remifentanil is a potent ultra-short acting μ-opioid analgesic drug, frequently used in anaesthesia due to its favorable pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profile. It may be associated with the occurrence of hyperalgesia. Preclinical studies suggest a potential role of microglia, although the molecular mechanisms have not been fully elucidated. Considering the role of microglia in brain inflammation and the relevant differences among species, the effects of remifentanil were studied on the human microglial C20 cells. The drug was tested at clinically relevant concentrations under basal and inflammatory conditions. In the C20 cells, the expression and secretion of interleukin 6, interleukin 8 and the monocyte chemotactic protein 1 were rapidly induced by a mixture of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This stimulatory effect was sustained up to 24 h. Remifentanil did not exert any toxic effect nor modify the production of these inflammatory mediators, thus suggesting the lack of direct immune modulatory actions on human microglia.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Cinzia Dello Russo, Natalia Cappoli, Elisabetta Tabolacci, Liliana Sollazzi, Pierluigi Navarra, Paola Aceto

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





