Streptozotocin as a tool for induction of rat models of diabetes
a practical guide
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2022-5720Keywords:
animal model, rat, streptozotocin, diabetesAbstract
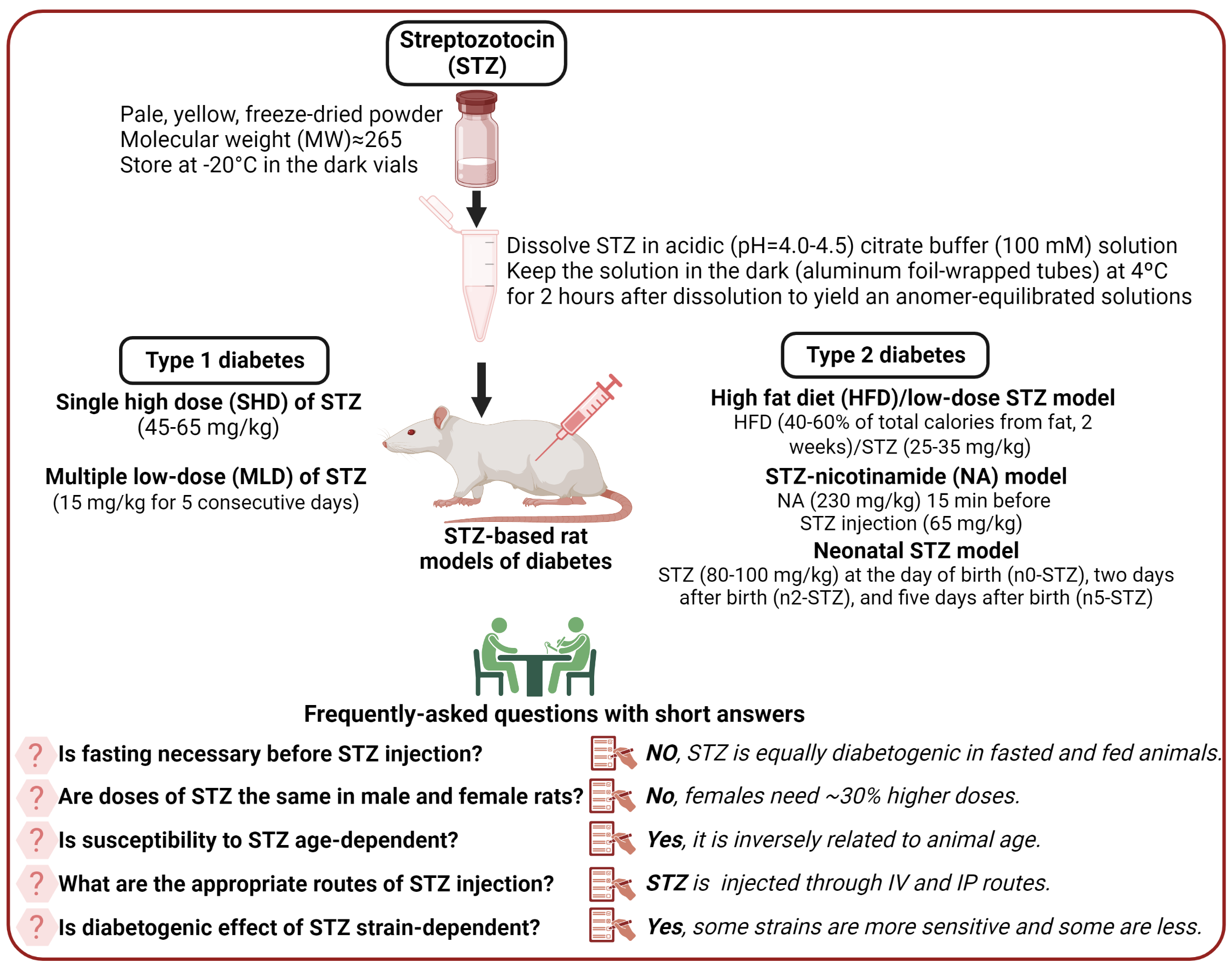
Streptozotocin (STZ) is the most used diabetogenic chemical for creating rat models of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Despite ~60 years of using STZ in animal diabetes research, some prevailing views about STZ preparation and use are not supported by evidence. Here, we provide practical guides for using STZ to induce diabetes in rats. Susceptibility to the diabetogenic effect of STZ is inversely related to age, and males are more susceptible to STZ than females. Wistar and Sprague-Dawley rats, the most commonly-used rat strains, are sensitive to STZ, but some strains (e.g., Wistar-Kyoto rats) are less sensitive. STZ is mostly injected intravenously or intraperitoneally, but its intravenous injection produces more stable hyperglycemia. Despite the prevailing view, no fasting is necessary before STZ injection, and injection of its anomer-equilibrated solutions (i.e., more than 2 hours of dissolving) is recommended. Mortality following the injection of diabetogenic doses of STZ is due to severe hypoglycemia (during the first 24 h) or severe hyperglycemia (24 h after the injection and onwards). Some measures to prevent hypoglycemia-related mortality in rats include providing access to food soon after the injection, administration of glucose/sucrose solutions during the first 24-48 h after the injection, administration of STZ to fed animals, and using anomer-equilibrated solutions of STZ. Hyperglycemia-related mortality following injection of high doses of STZ can be overcome with insulin administration. In conclusion, STZ is a valuable chemical for inducing diabetes in rats, but some practical guides should be considered to perform well-conducted and ethical studies.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Asghar Ghasemi, Sajad Jeddi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





