Astaxanthin improves fatty acid dysregulation in diabetes by controlling the AMPK-SIRT1 pathway
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2023-6132Keywords:
astaxanthin, diabetes mellitus, SIRT1, AMPK, fatty acids profileAbstract
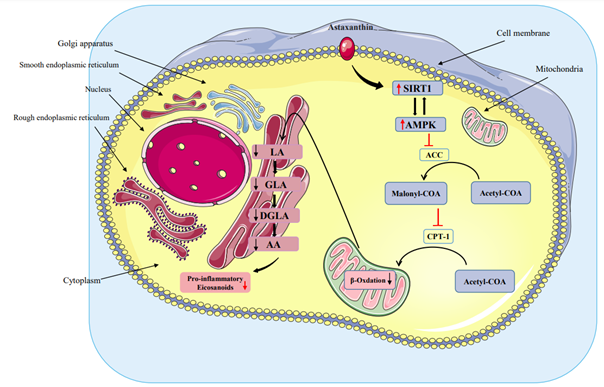
Due to the rising prevalence of metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes (T2DM), new prevention and treatment strategies are needed. The aim was to examine the effect of astaxanthin (AST) on the major regulatory metabolism pathway SIRT-MAPK and fatty acid (FA) profile of plasma in patients with T2DM. This clinical trial included 68 T2DM patients randomly assigned to receive 10 mg/day of oral AST (n = 34) or placebo (n = 33) for 12 weeks. The expression level of SIRT1, AMPK activity, and the level of fatty acids in the serum were examined. The results showed that AST could modify the serum levels of saturated fatty acids (SFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), particularly that of Arachidonic acid, from 11.31±0.35 to 8.52±0.72 %. Also, AST increased the expression and activity levels of SIRT1 and AMPK, respectively. Pearson analysis also revealed a significant association between AMPK activity and Linoleic acid serum (LA) levels (~ -0.604, p~0.013). AST can modify the FA profile of plasma by inducing metabolizing cells to uptake them. Also, it can activate the SIRT-AMPK pathway related to metabolism regulation.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Sana Taghiyar, Fatemeh Pourrajab, Mohammad Hosein Aarabi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





