The bridge between cell survival and cell death
reactive oxygen species-mediated cellular stress
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2023-6221Keywords:
Redox homeostasis, antioxidant defense systems, Nrf2, oxidative and reductive stress,, cell death pathways, mitohormesisAbstract
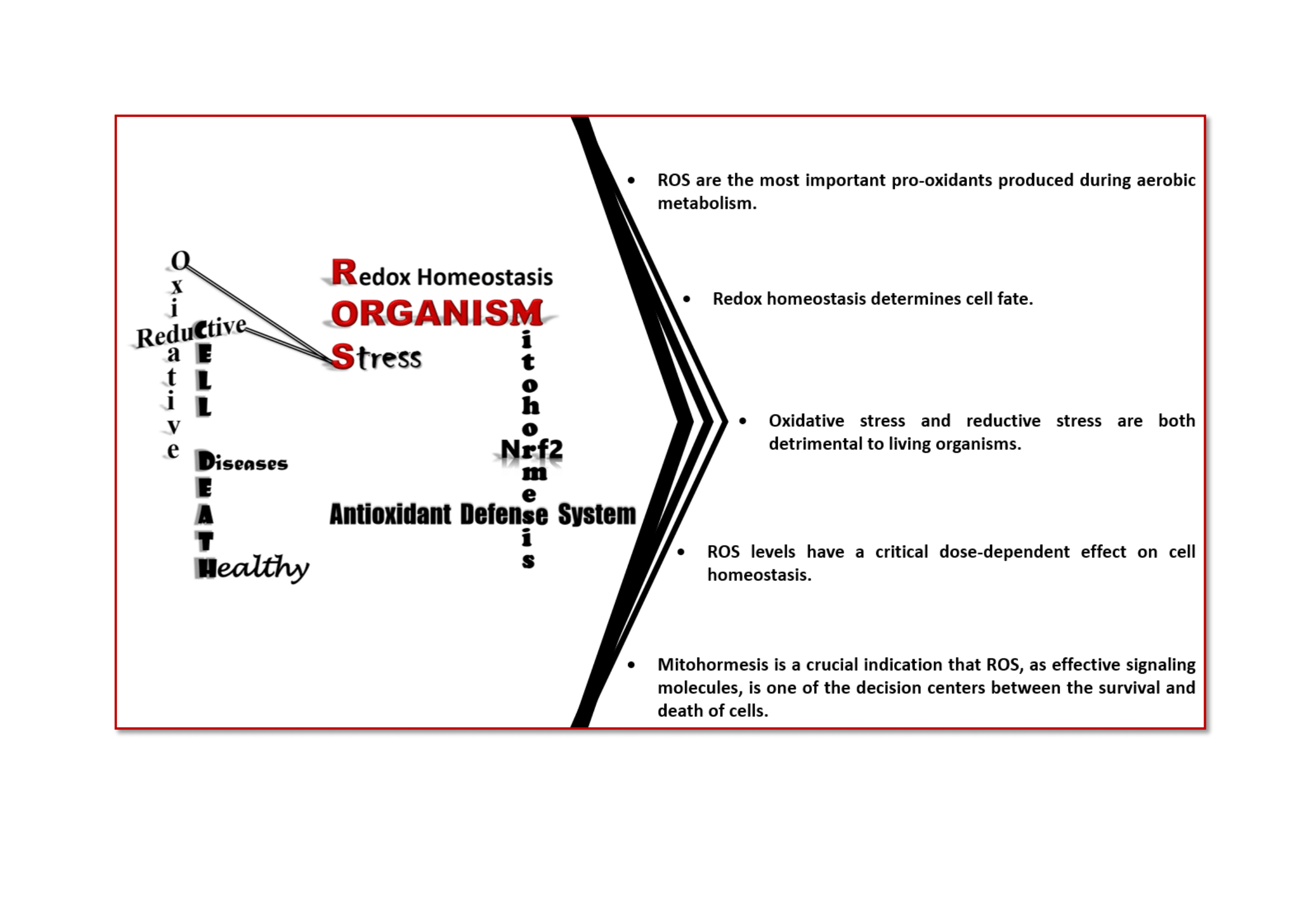
As a requirement of aerobic metabolism, regulation of redox homeostasis is indispensable for the continuity of living homeostasis and life. Since the stability of the redox state is necessary for the maintenance of the biological functions of the cells, the balance between the pro-oxidants, especially ROS and the antioxidant capacity is kept in balance in the cells through antioxidant defense systems. The pleiotropic transcription factor, Nrf2, is the master regulator of the antioxidant defense system. Disruption of redox homeostasis leads to oxidative and reductive stress, bringing about multiple pathophysiological conditions. Oxidative stress characterized by high ROS levels causes oxidative damage to biomolecules and cell death, while reductive stress characterized by low ROS levels disrupt physiological cell functions. The fact that ROS, which were initially attributed as harmful products of aerobic metabolism, at the same time function as signal molecules at non-toxic levels and play a role in the adaptive response called mithormesis points out that ROS have a dose-dependent effect on cell fate determination.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Neşe Vardar Acar, Riza Köksal Özgül

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





