Intraperitoneal hepato-renal toxicity of zinc oxide and nickel oxide nanoparticles in male rats
biochemical, hematological and histopathological studies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2023-6237Keywords:
nanoparticles, zinc oxide, nickel oxide, hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, intraperitoneal routeAbstract
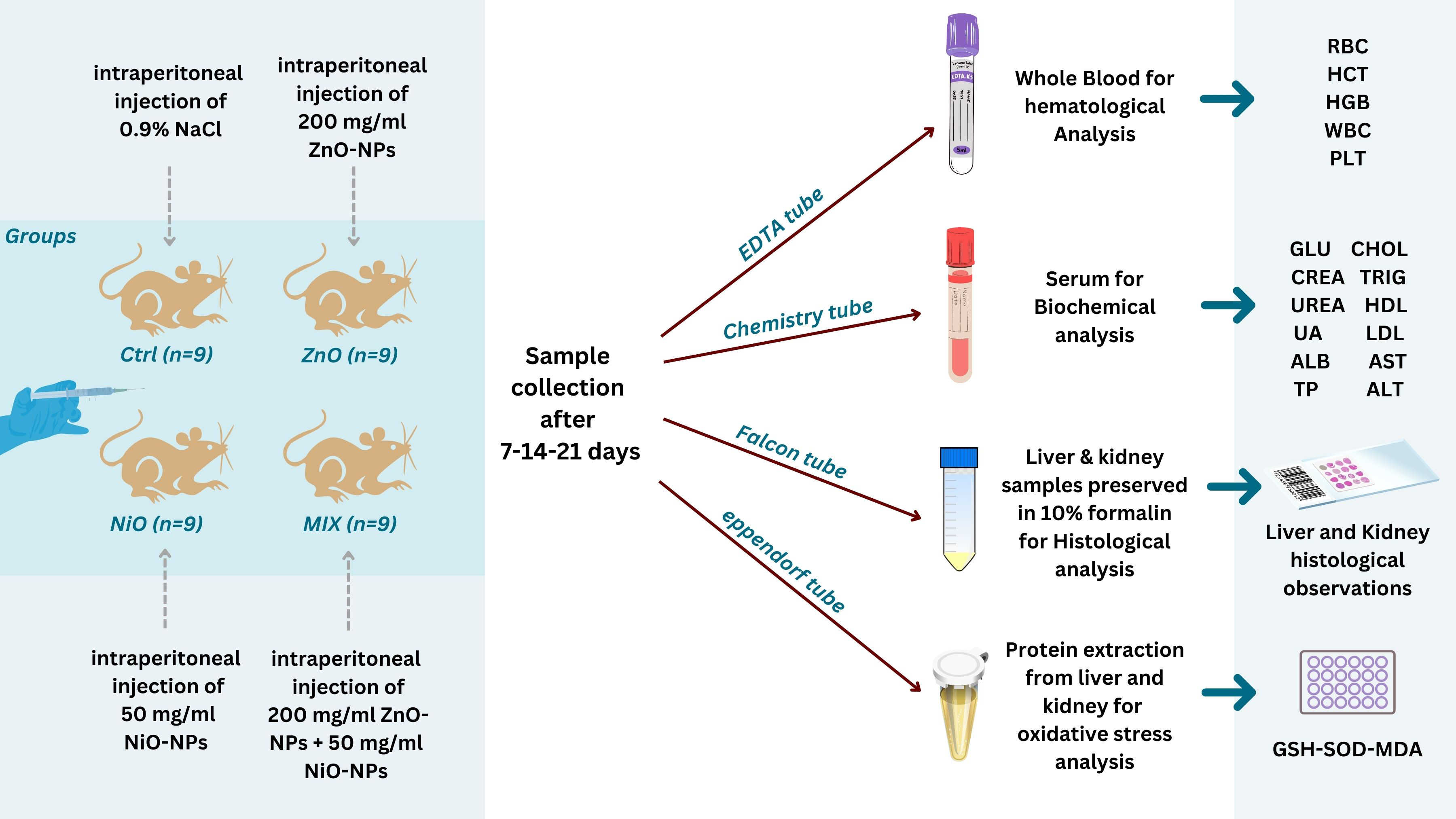
In recent years, zinc oxide (ZnO) and nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticles (NPs) have become more prevalent in commercial and industrial products. However, questions have been raised regarding their potential harm to human health. Limited studies have been conducted on their intraperitoneal toxicity in rats, and their co-exposure effects remain uncertain. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate some biological responses induced by a single intraperitoneal injection of ZnO-NPs (200 mg/kg) and/or NiO-NPs (50 mg/kg) in rats over time intervals. Blood and organ samples were collected from 36 male rats for hematological, biochemical, oxidative stress, and histological analysis. Results showed that the administration of NPs reduced the body and organ weights as well as red blood cell (RBC) indices and altered white blood cell (WBC) and platelet (PLT) counts. The experimental groups exhibited elevated levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), creatinine (CREA), urea, lipid profile, glucose (GLU), total protein (TP), albumin (ALB) and malondialdehyde (MDA), and decreased uric acid (UA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione (GSH). Histological observations also revealed architectural damages in liver and kidneys. These alterations were time-dependent and varied in their degree of toxicity. Co-exposure of NPs initially lessened the damage but increased it afterwards compared to individual exposure. In conclusion, intraperitoneal injection of ZnO-NPs and/or NiO-NPs alters biological processes and induces oxidative stress in rats’ liver and kidneys in a time-dependent manner, with NiO-NPs being more potent than ZnO-NPs. Furthermore, co-exposed NPs initially appeared to be antagonistic to one another while further aiming toward synergism.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Noura S. Abouzeinab, Nour Kahil, Najla Fakhruddin, Ramadan Awad, Mahmoud I. Khalil

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





