Exploring mito-nuclear genetic factors in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy
insights from comprehensive profiling of unique cases
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2023-6297Keywords:
mitochondrial complex I disorder, retinoganglion degeneration, mito-nuclear genetic factors, arLHON, optic atrophy and vision lossAbstract
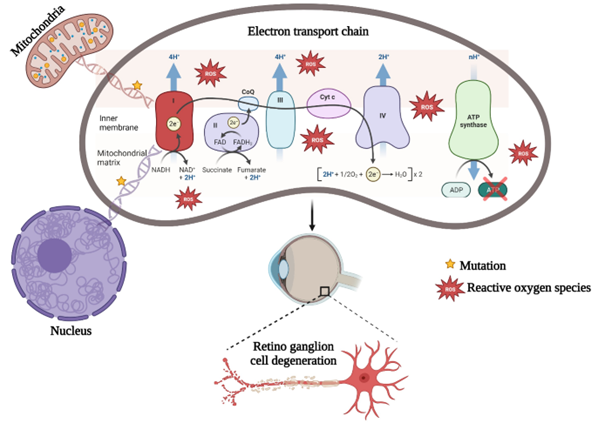
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a mitochondrial complex I disorder and causes inexorable painless vision loss. Recent studies from India reported that a significant proportion of LHON patients lack primary mitochondrial DNA mutations, suggesting that alternative genetic factors contribute to disease development. Therefore, this study investigated the genetic profile of LHON-affected individuals in order to understand the role of mito-nuclear genetic factors in LHON. A total of thirty probands displaying symptoms consistent with LHON have undergone whole mitochondrial and whole exome sequencing. Interestingly, whole mtDNA sequencing revealed primary mtDNA mutations in 30 % of the probands (n=9), secondary mtDNA mutations in 40 % of the probands (n=12) and no mitochondrial changes in 30 % of individuals (n=9). Further, WES analysis determined pathogenic mutations in 11 different nuclear genes, especially in cases with secondary mtDNA mutations (n=6) or no mtDNA mutations (n=6). These findings provide valuable insight into LHON genetic predisposition, particularly in cases lacking primary mtDNA mutations.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Prakash Chermakani, Poigaialwar Gowri, Shanmugam Mahesh Kumar, Periasamy Sundaresan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





