Phosphatidylcholine (PCL) fortified nano-phytopharmaceuticals for improvement of therapeutic efficacy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2023-6345Keywords:
phytopharmaceuticals, phosphatidylcholine, nano-formulations, anti-cancer, antioxidantAbstract
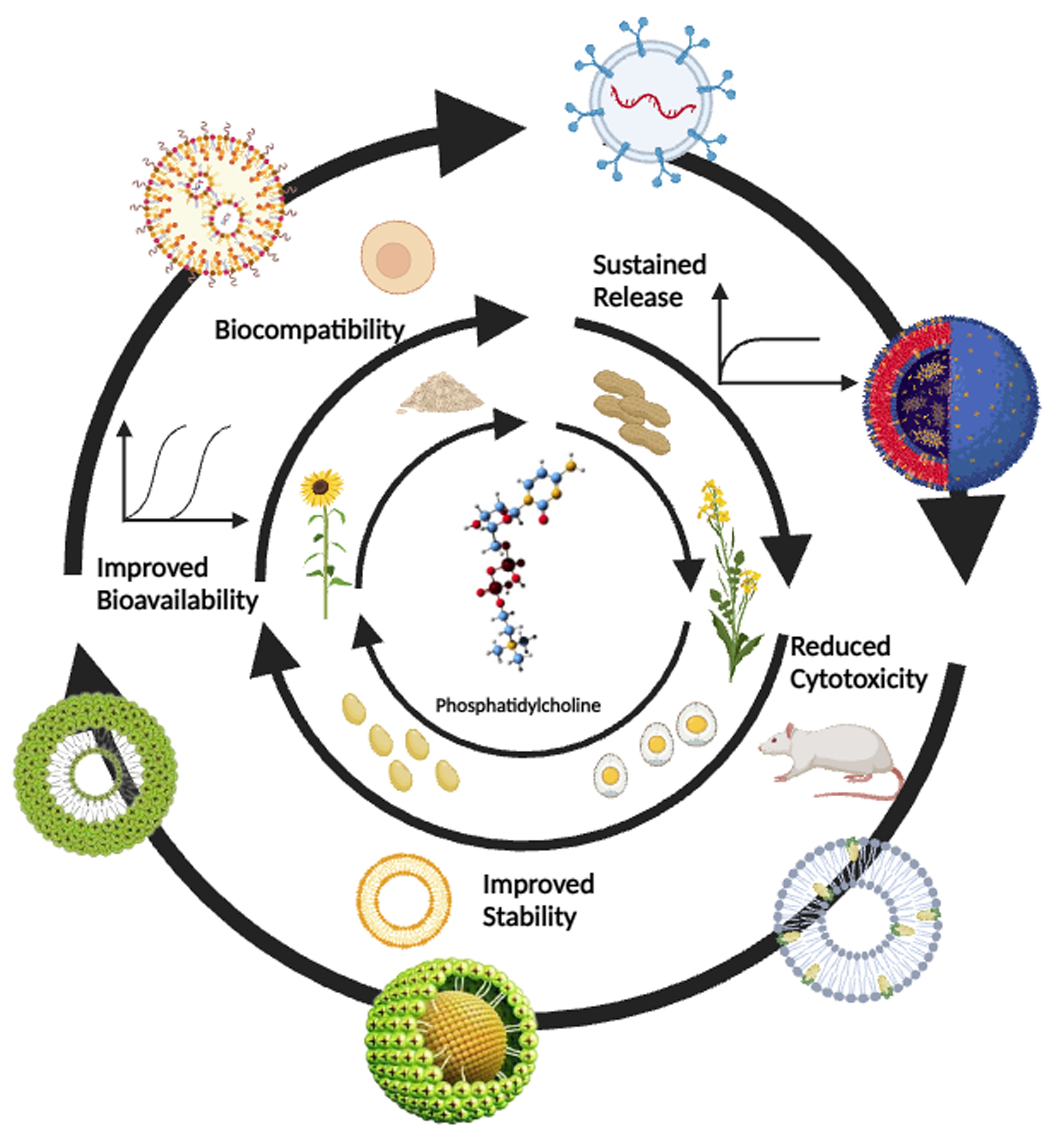
Phytopharmaceuticals, derived from plants, are increasingly recognized for their potential therapeutic benefits. However, their effectiveness is often hindered by challenges such as poor bioavailability, stability, and targeted delivery. In this study, we aimed to address these limitations by developing PCL (phosphatidylcholine) fortified nano-phytopharmaceuticals to enhance therapeutic efficacy. PCL, a biocompatible and biodegradable polymer, was employed to encapsulate the phytopharmaceuticals, thereby improving their stability and bioavailability. The encapsulation process utilized nanoprecipitation, resulting in the formation of nanoparticles with controlled size and morphology. Various analytical techniques were employed to characterize the physicochemical properties of PCL fortified nano-phytopharmaceuticals, including dynamic light scattering, scanning electron microscopy, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Furthermore, the release kinetics of encapsulated phytopharmaceuticals from PCL nanoparticles were evaluated, demonstrating sustained and controlled release profiles, essential for prolonged therapeutic effects. Cytotoxicity studies conducted on in vitro cell culture models confirmed the biocompatibility and non-toxic nature of the developed nano-phytopharmaceuticals. Additionally, in vivo studies were conducted to assess the therapeutic efficacy of PCL fortified nano-phytopharmaceuticals in animal models. The results showIased improved bioavailability, targeted tissue distribution, and enhanced therapeutic effects compared to free phytopharmaceuticals. Moreover, the developed nano-phytopharmaceuticals exhibited prolonged circulation time in the bloodstream, enabling improved drug delivery and reduced dosing frequency. This review highlights the promising potential of PCL fortified nano-phytopharmaceuticals as an effective approach for enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of phytopharmaceuticals. The improved stability, bioavailability, sustained release, and targeted delivery achieved through this formulation strategy offer promising opportunities for advancing plant-based therapies.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Devesh U. Kapoor, Mansi Gaur, Akshay Parihar, Bhupendra G. Prajapati, Sudarshan Singh, Ravish J. Patel

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





