Structural and molecular characterization of lopinavir and ivermectin as breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) inhibitors
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2023-6427Keywords:
ABCG2, drug repositioning, lopinavir, ivermectin, molecular modellingAbstract
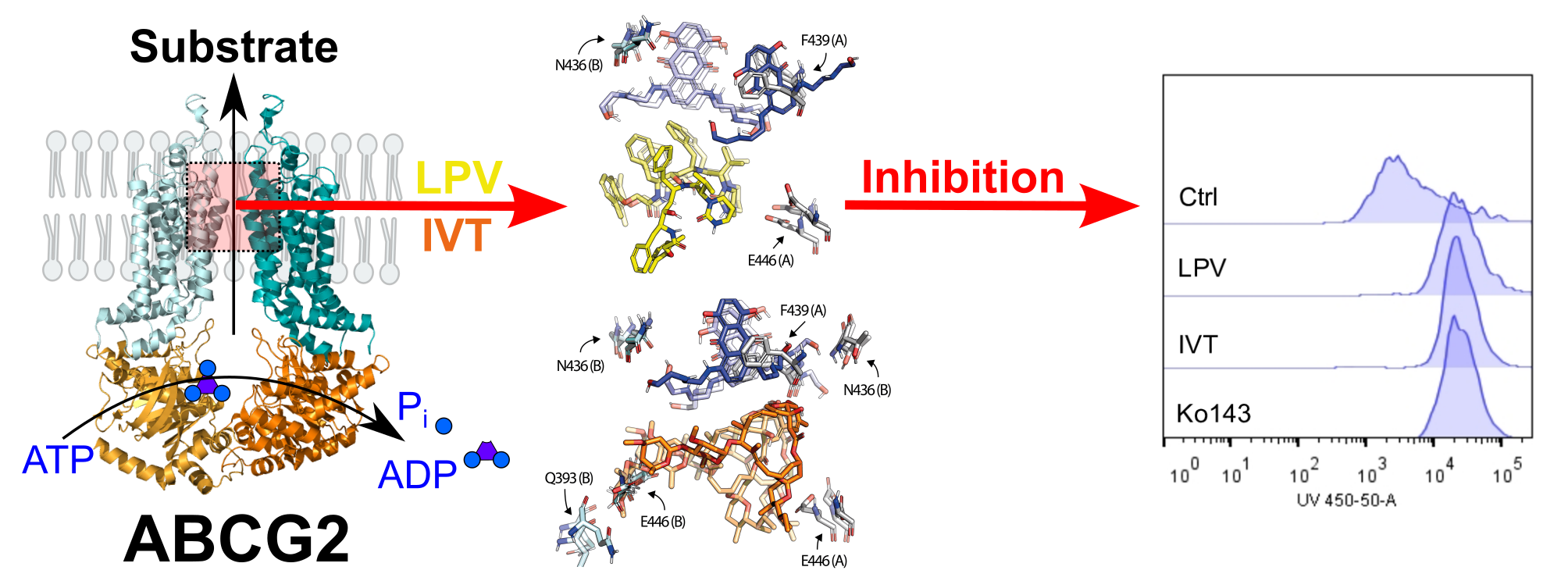
A current clinical challenge in cancer is multidrug resistance (MDR) mediated by ABC transporters. Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) or ABCG2 transporter is one of the most important ABC transporters implicated in MDR and the use of inhibitors is a promising approach to overcome the resistance in cancer. This study aimed to characterize the molecular mechanism of ABCG2 inhibitors identified by a repurposing drug strategy using antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antiparasitic agents. Lopinavir and ivermectin can be considered as pan-inhibitors of ABC transporters, since both compounds inhibited ABCG2, P-glycoprotein and MRP1. They inhibited ABCG2 activity showing IC50 values of 25.5 and 23.4 µM, respectively. These drugs were highly cytotoxic and not transported by ABCG2. Additionally, these drugs increased the 5D3 antibody binding and did not affect the mRNA and protein expression levels. Cell-based analysis of the type of inhibition suggested a non-competitive inhibition, which was further corroborated by in silico approaches of molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. These results showed an overlap of the lopinavir and ivermectin binding sites on ABCG2, mainly interacting with E446 residue. However, the substrate mitoxantrone occupies a different site, binding to the F436 region, closer to the L554/L555 plug. In conclusion, these results revealed the mechanistic basis of lopinavir and ivermectin interaction with ABCG2.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Julia de Paula Dutra, Gustavo Scheiffer, Thales Kronenberger, Lucas Julian Cruz Gomes, Isadora Zanzarini, Kelly Karoline dos Santos, Arun K. Tonduru, Antti Poso, Fabiane Gomes de Moraes Rego, Geraldo Picheth, Glaucio Valdameri, Vivian Rotuno Moure

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





