Promising influences of hesperidin and hesperetin against diabetes and its complications
a systematic review of molecular, cellular, and metabolic effects
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2023-6577Keywords:
hesperidin, hesperetin, diabetes, diabetes complications, inflammation, oxidative stressAbstract
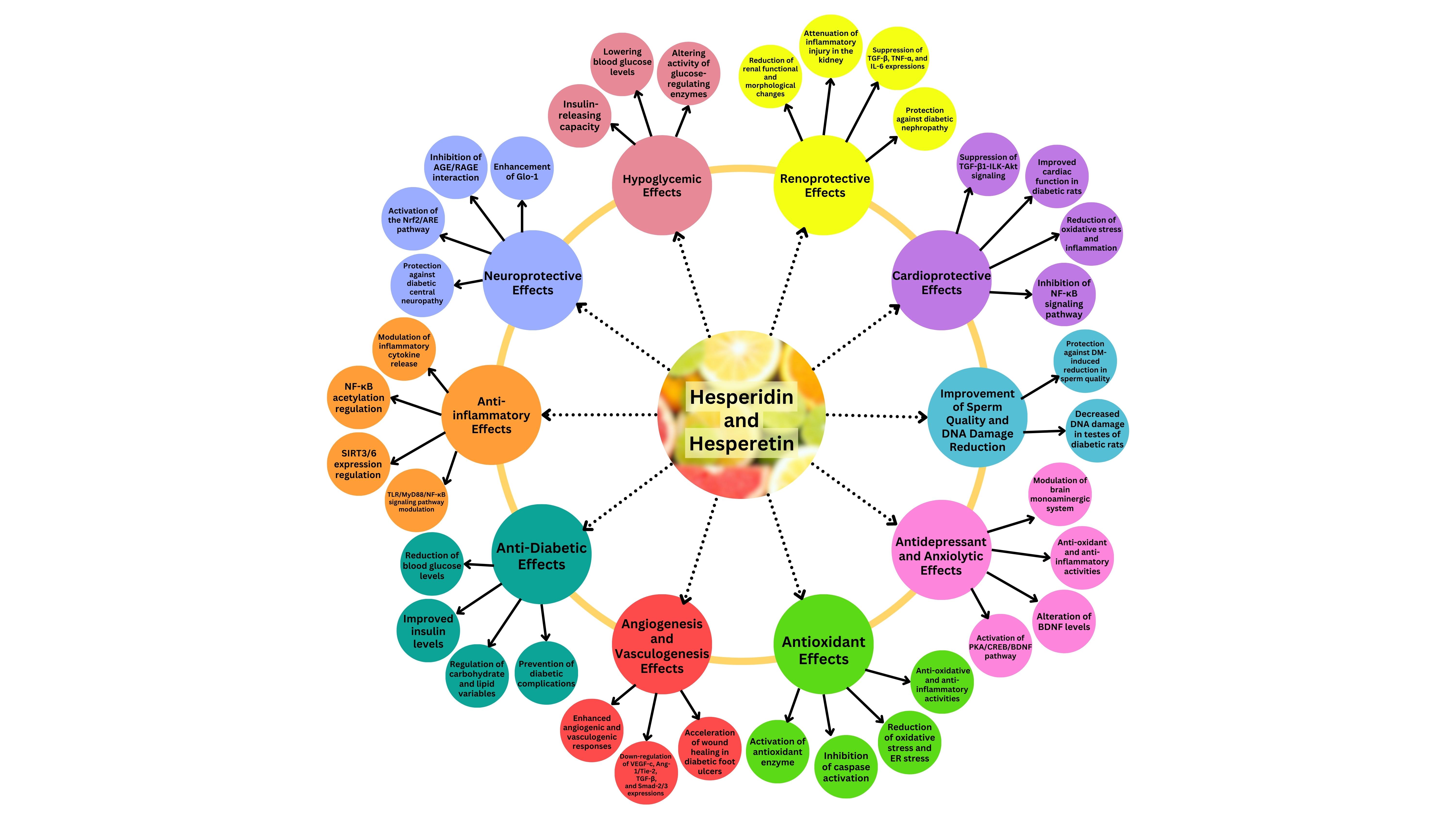
Hesperidin and hesperetin, two flavonoids with potential therapeutic value, have been extensively studied in the context of diabetes management. The main objective of this research is to ascertain their potential as therapeutic options for managing diabetes and its complications. The present study utilized a systematic review methodology and comprehensively explored relevant literature from databases, including PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, from inception until July 2023. The review summarized the outcomes related to the molecular, cellular, and metabolic effects of hesperidin and hesperetin in diabetes and its complications. Hesperetin exhibits a potential treatment for preventing diabetes and its associated complications through modulation of inflammatory cytokine release and expression via the pathway of signaling through Toll-like receptor/Myeloid differentiation factor 88/Nuclear factor-kappa B. Hesperidin shows promise as a biomolecule for treating diabetic neuropathy, primarily through activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf-2), as an antioxidant-response element signaling, leading to neuroprotective effects. Both compounds demonstrated the ability to normalize blood glucose levels and reduce serum and liver lipid levels, making them potential candidates for managing hypoglycemia and hypolipidemia in diabetes. Hesperidin also showed potential benefits against diabetic nephropathy by suppressing transforming growth factor-β1-integrin-linked kinase-Akt signaling and enhancing renal function. Furthermore, hesperidin's antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-depressant effects in diabetic conditions expanded its potential therapeutic applications. This systematic review provides substantial evidence supporting the consideration of hesperidin and hesperetin for diabetes and its complications. It offers exciting possibilities for developing novel, cost-effective treatment options to enhance diabetes management and patient outcomes.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Amirhossein Mirzaei, Ali Mirzaei, Shakiba Najjar Khalilabad, Vahid Reza Askari, Vafa Baradaran Rahimi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





