Momordicine I suppresses glioma growth by promoting apoptosis and impairing mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2023-6129Keywords:
glioblastoma, Momordica charantia, momordicine I, oxidative phosphorylation capacity, DLGPA5Abstract
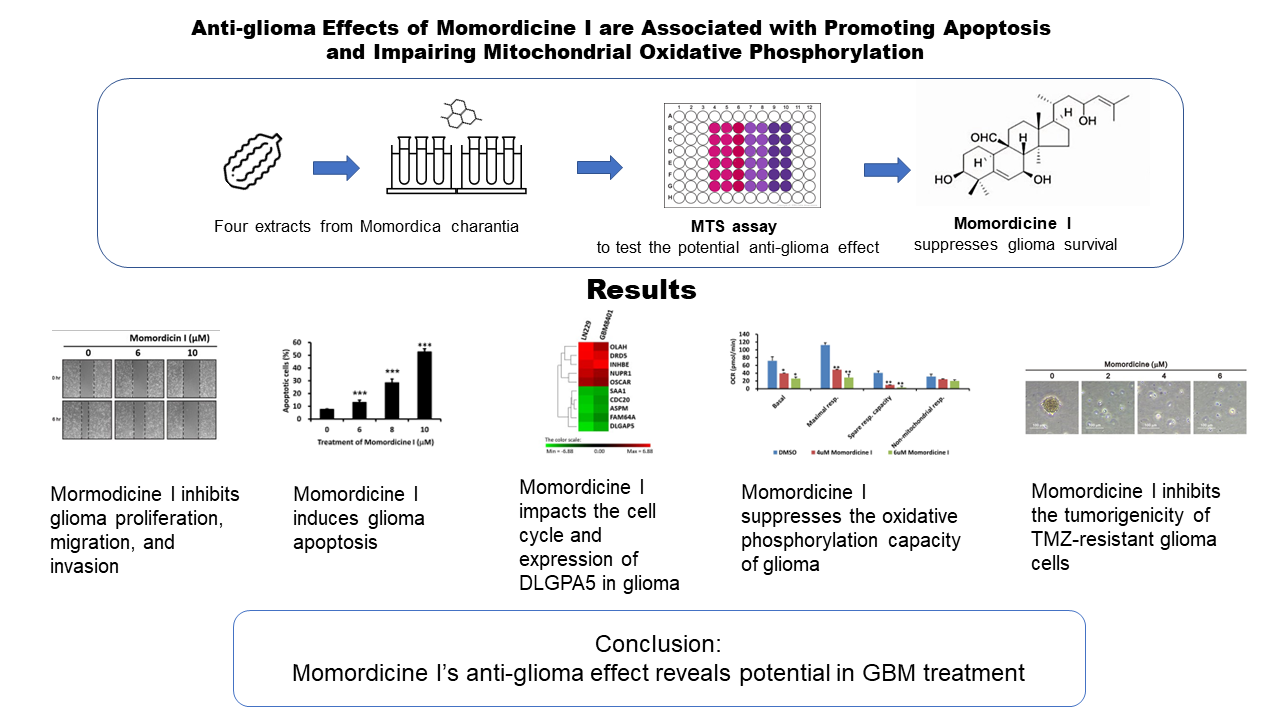
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common type of primary brain tumor. Patients with GBM have poor survival outcomes. Isolated components of Momordica charantia have anticancer effects. However, the bioactivity of M. charantia extracts against GBM remains unknown. We tested four major extracts of M. charantia and found that momordicine I reduced glioma cell viability without serious cytotoxic effects on astrocytes. Momordicine I suppressed glioma cell colony formation, proliferation, migration, and invasion. Momordicine I also induced apoptosis, intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and senescence in glioma cells. Moreover, momordicine I decreased the oxidative phosphorylation capacity of glioma cells and inhibited tumor sphere formation in temozolomide (TMZ)-resistant GBM cells. We further explored whether the antiglioma effect of momordicine I may be related to cell cycle modulation and DLGPA5 expression. Our results indicate that the cytotoxic effect of momordicine I on glioma cells suggests its potential therapeutic application to GBM treatment.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ying Kao, Chung-Hsing Chou, Li-Chun Huang, Chia-Kuang Tsai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The authors keep the copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license, CC BY 4.0. This licencse permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
- The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations.
- Because the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate at the time of publication, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions presented in the publication. The publisher makes no guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
- The authors can enter into additional contracts for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version by citing the initial publication in this journal (e.g. publishing in an institutional repository or in a book).





